Python API
You can program AUVs using the Python language.
Installation
Using pip
pip install naus
From source
Inside the repository, run:
pip install ./python
Usage
Initialization
To get started, initialize an AUV object:
import naus
auv = naus.AUV(0)
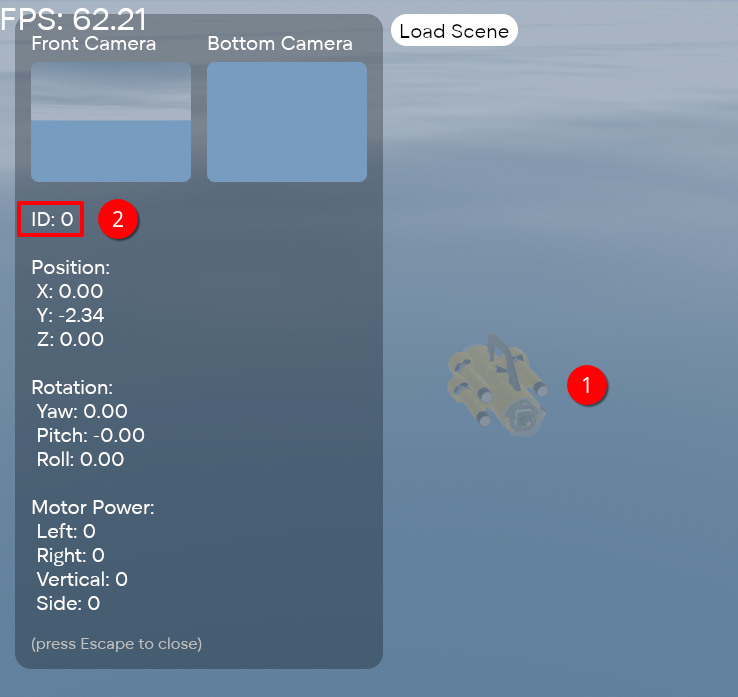
The argument is the AUV's ID. You can find it by clicking on the AUV in the simulator:
Getting telemetry
Use the get_telemetry method to get telemetry data. Method definition:
def get_telemetry(self) -> Telemetry:
...
The Telemetry object is a dataclass that contains the AUV's world coordinates and orientation (yaw, pitch, roll):
class Telemetry:
x: float
y: float
z: float
yaw: float
pitch: float
roll: float
The Y-axis represents depth and is oriented upward in world space. This means Y is negative for a submerged AUV.
Example:
telemetry = auv.get_telemetry()
print(telemetry) # Telemetry(x=1.2, y=3.4, z=5.6, yaw=7.8, pitch=9.0, roll=4.2)
Controlling thrusters
Use the set_motor_powers method to control the AUV's thrusters:
def set_motor_powers(
self,
*,
left: int | None = None,
right: int | None = None,
side: int | None = None,
vertical: int | None = None,
) -> None:
...
The parameters left, right, side, and vertical control the thrust of the corresponding motors. Values must be between -100 and 100 (inclusive).
Examples:
# Move forward with 75% thrust:
auv.set_motor_powers(left=75, right=75)
# Rotate in place with 50% thrust:
auv.set_motor_powers(left=50, right=-50)
# Stop all thrusters:
auv.set_motor_powers(left=0, right=0, side=50, vertical=0)
Getting camera images
To get images from the AUV's cameras, use the get_images method. It returns a tuple of two BGR matrices: the front and bottom camera images.
def get_images(self) -> tuple[MatLike, MatLike]:
Image resolution is fixed at 320×240 pixels. The images are compatible with OpenCV and NumPy.
Example:
import cv2 as cv
import numpy as np
img_front, img_bottom = auv.get_images()
stack = cv.vstack([img_front, img_bottom]) # stack images vertically
cv.imshow("Images", stack)
cv.waitKey(0) # wait for a key press
Programming Approach
The simplest approach is an infinite loop where telemetry is read and the AUV state is updated (including thruster control):
import naus
import time
auv = naus.AUV(0)
while True:
telemetry = auv.get_telemetry()
img_front, img_bottom = auv.get_images()
# <process telemetry>
# <apply computer vision>
# <update internal state>
# <adjust motor powers>
time.sleep(0.01) # ~100 Hz loop
To control multiple AUVs in the same program, use multithreading:
import naus
import threading
def foo() -> None:
auv = naus.AUV(0)
...
def bar() -> None:
auv = naus.AUV(1)
...
def baz() -> None:
auv = naus.AUV(2)
...
tasks = [
threading.Thread(target=foo),
threading.Thread(target=bar),
threading.Thread(target=baz),
]
for t in tasks:
t.start()
Refer to the Python threading module documentation for more information.